42 tissue type
Bone Tissue Type, Function & Location - Study.com 11.8.2021 · Osteocytes are the most abundant type of cell in bone tissue, making up about 95% of the total cells. They are formed from osteoblasts that get trapped within bone tissue as it forms. Human leukocyte antigen - Wikipedia The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) found in many animals.. Mutations in HLA genes may be linked to autoimmune …
Meristem - Wikipedia The meristem is a type of tissue found in plants. It consists of undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells) capable of cell division.Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants.

Tissue type
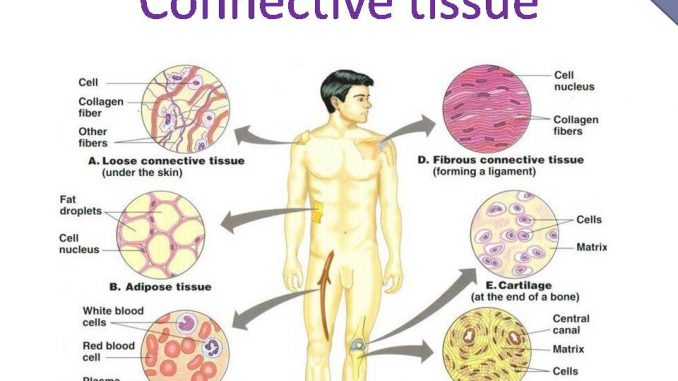
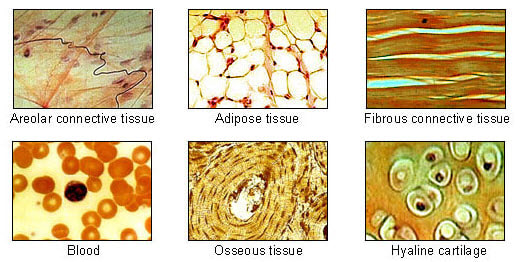
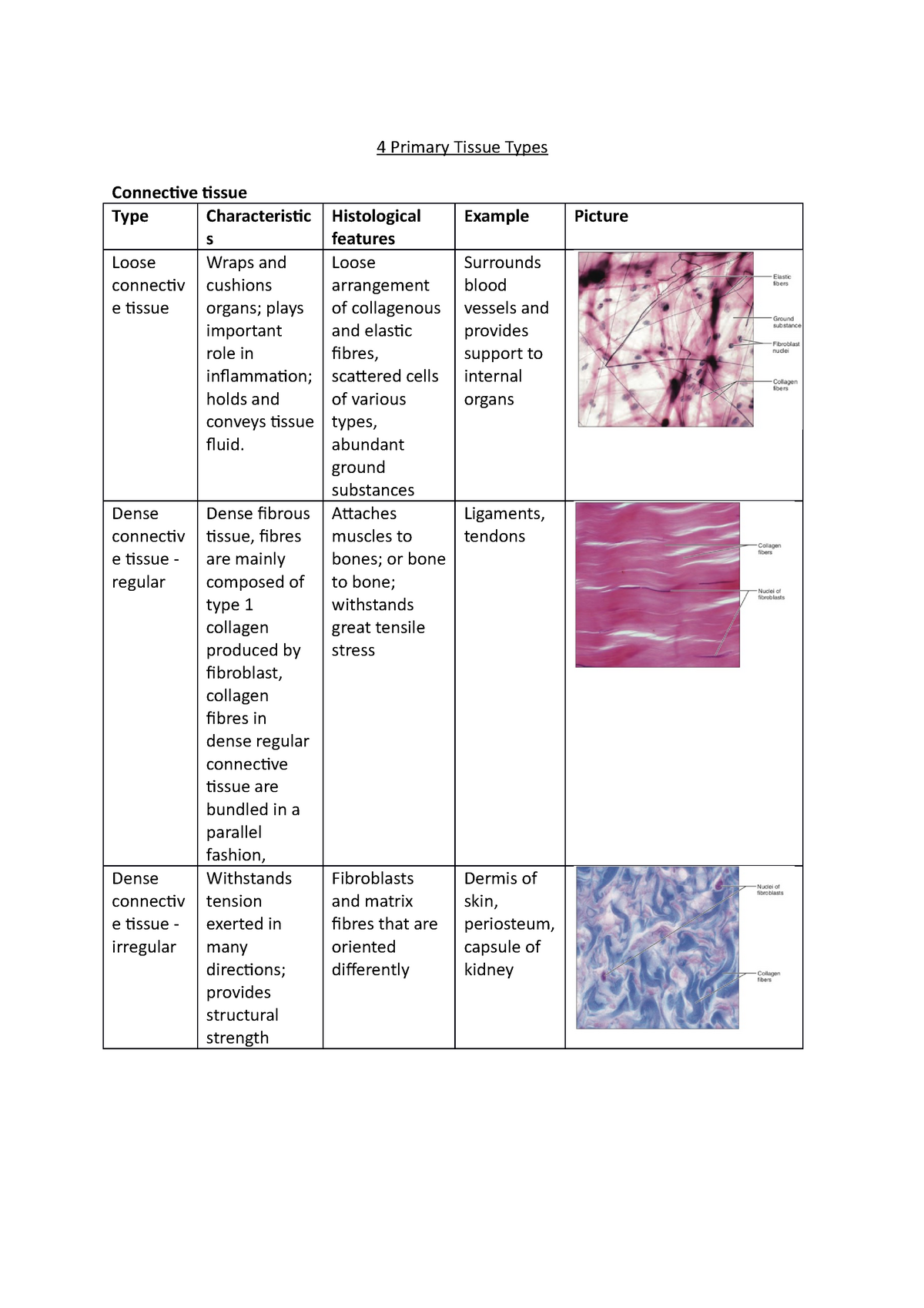
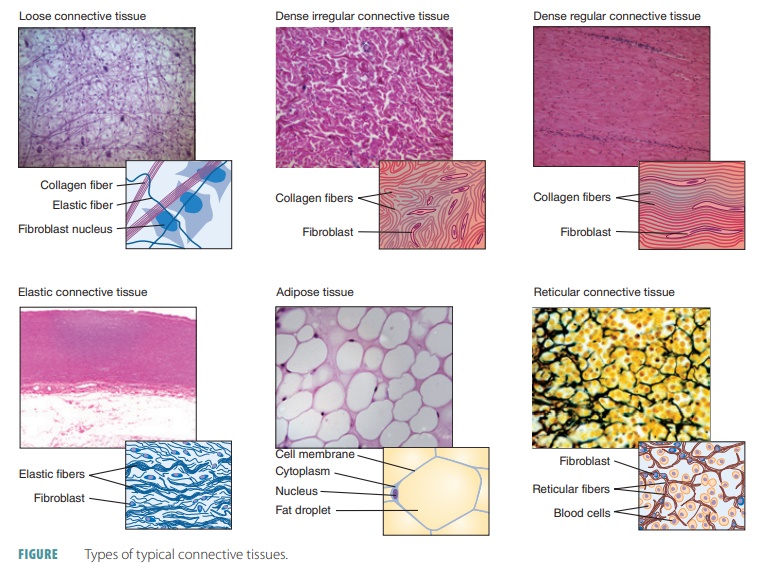
Adipose tissue - Wikipedia In humans, adipose tissue is located: beneath the skin (subcutaneous fat), around internal organs (visceral fat), in bone marrow (yellow bone marrow), intermuscular (Muscular system) and in the breast (breast tissue).Adipose tissue is found in specific locations, which are referred to as adipose depots.Apart from adipocytes, which comprise the highest percentage of cells within … Brown adipose tissue - Wikipedia Brown adipose tissue (BAT) or brown fat makes up the adipose organ together with white adipose tissue (or white fat). ... Whilst believed by many to be a type of gland, it is actually a collection of adipose tissues lying between the scapulae of rodentine mammals. Difference Between Loose and Dense Connective Tissue Sep 19, 2017 · What is Loose Connective Tissue. Loose connective tissue is a type of connective tissue with loosely arranged collagen fibers. However, it consists of many cells. Loose connective tissue is the most common type of connective tissue in vertebrates and it holds the organs in place and attaches the epithelial tissue to the underlying tissues. It ...
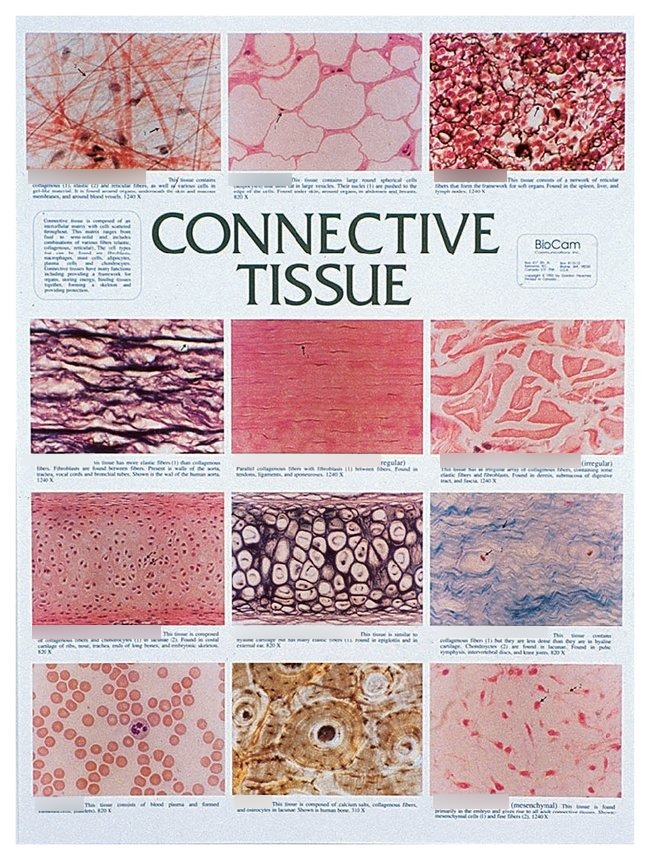
Tissue type. Type Deep Tissue Injury (DTI) Stage I Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 ... Oct 09, 2017 · the extent of tissue loss this is an Unstageable Pressure Injury. Full-thickness skin and tissue loss in which the extent of tissue damage within the ulcer cannot be confirmed because it is obscured by slough or eschar. If slough or eschar is removed, a Stage 3 or Stage 4 pressure injury will be revealed. Stable eschar (i.e. dry, adherent, intact Tissue (biology) - Wikipedia In biology, tissue is a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ.A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" derives from the French word "tissu", the past … Bulk tissue cell type deconvolution with multi-subject single-cell ... Jan 22, 2019 · Bulk tissue RNA-seq data reveals transcriptomic profiles but masks the contributions of different cell types. Here, the authors develop a new method for estimating cell type proportions from bulk ... Connective tissue - Wikipedia Another type of relatively undifferentiated connective tissue is the mucous connective tissue known as Wharton's jelly, found inside the umbilical cord. [22] : 160 Various types of specialized tissues and cells are classified under the spectrum of connective tissue, and are as diverse as brown and white adipose tissue , blood , cartilage and bone .
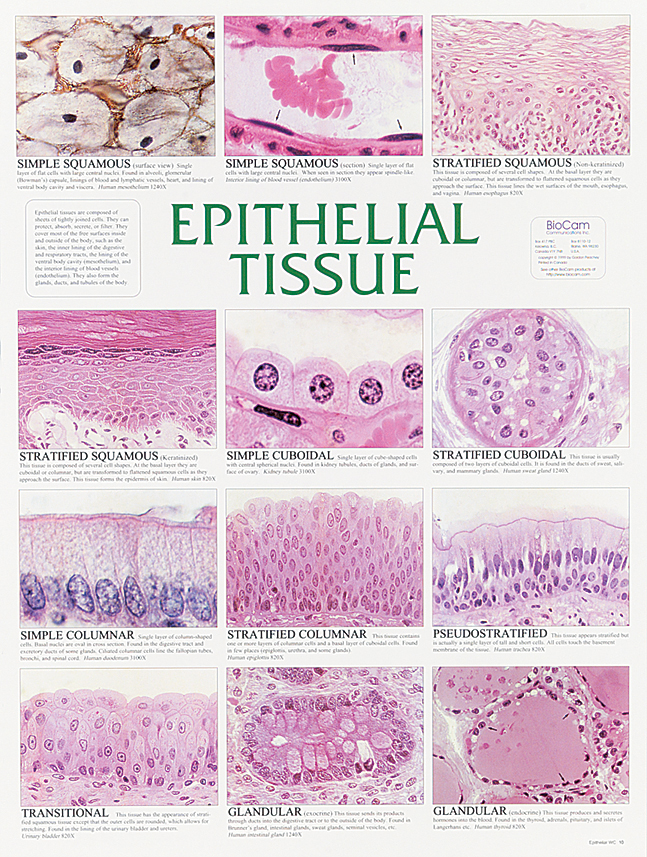
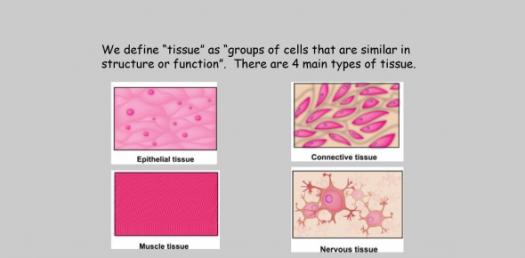
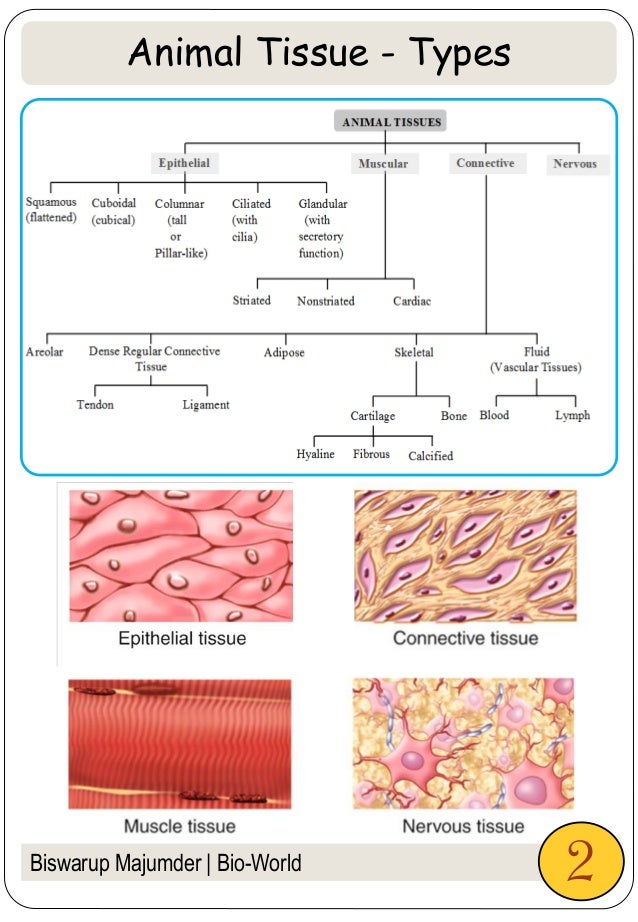
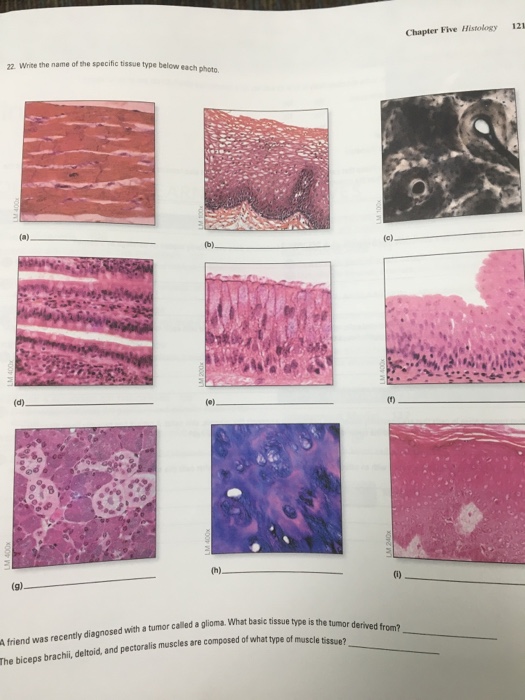
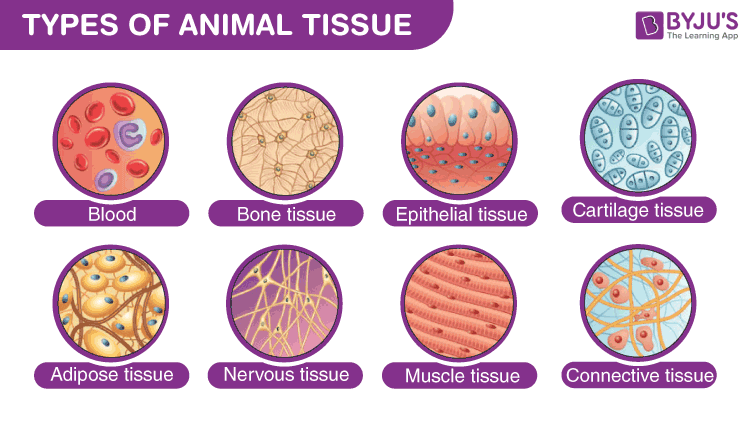
Epithelium - Wikipedia Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue.It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix.Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. Treatment by Cancer Type Guidelines COVID-19 Resources Treatment by Cancer Type Detection, Prevention, and Risk Reduction Supportive Care Specific Populations Guidelines for Patients Guidelines With Evidence Blocks NCCN Framework For Resource Stratification Harmonized Guidelines International Adaptations and Translations NCCN Mobile Apps Guidelines Process Guidelines ... Collagen - Wikipedia Collagen (/ ˈ k ɒ l ə dʒ ə n /) is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues.As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content. Collagen consists of amino acids bound together to form a triple helix of elongated fibril … Difference Between Loose and Dense Connective Tissue Sep 19, 2017 · What is Loose Connective Tissue. Loose connective tissue is a type of connective tissue with loosely arranged collagen fibers. However, it consists of many cells. Loose connective tissue is the most common type of connective tissue in vertebrates and it holds the organs in place and attaches the epithelial tissue to the underlying tissues. It ...
Brown adipose tissue - Wikipedia Brown adipose tissue (BAT) or brown fat makes up the adipose organ together with white adipose tissue (or white fat). ... Whilst believed by many to be a type of gland, it is actually a collection of adipose tissues lying between the scapulae of rodentine mammals. Adipose tissue - Wikipedia In humans, adipose tissue is located: beneath the skin (subcutaneous fat), around internal organs (visceral fat), in bone marrow (yellow bone marrow), intermuscular (Muscular system) and in the breast (breast tissue).Adipose tissue is found in specific locations, which are referred to as adipose depots.Apart from adipocytes, which comprise the highest percentage of cells within …














:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/reticular-fibers/67WQFPVEkHiYdw0ZPOGtQ_Reticular_fibers.png)
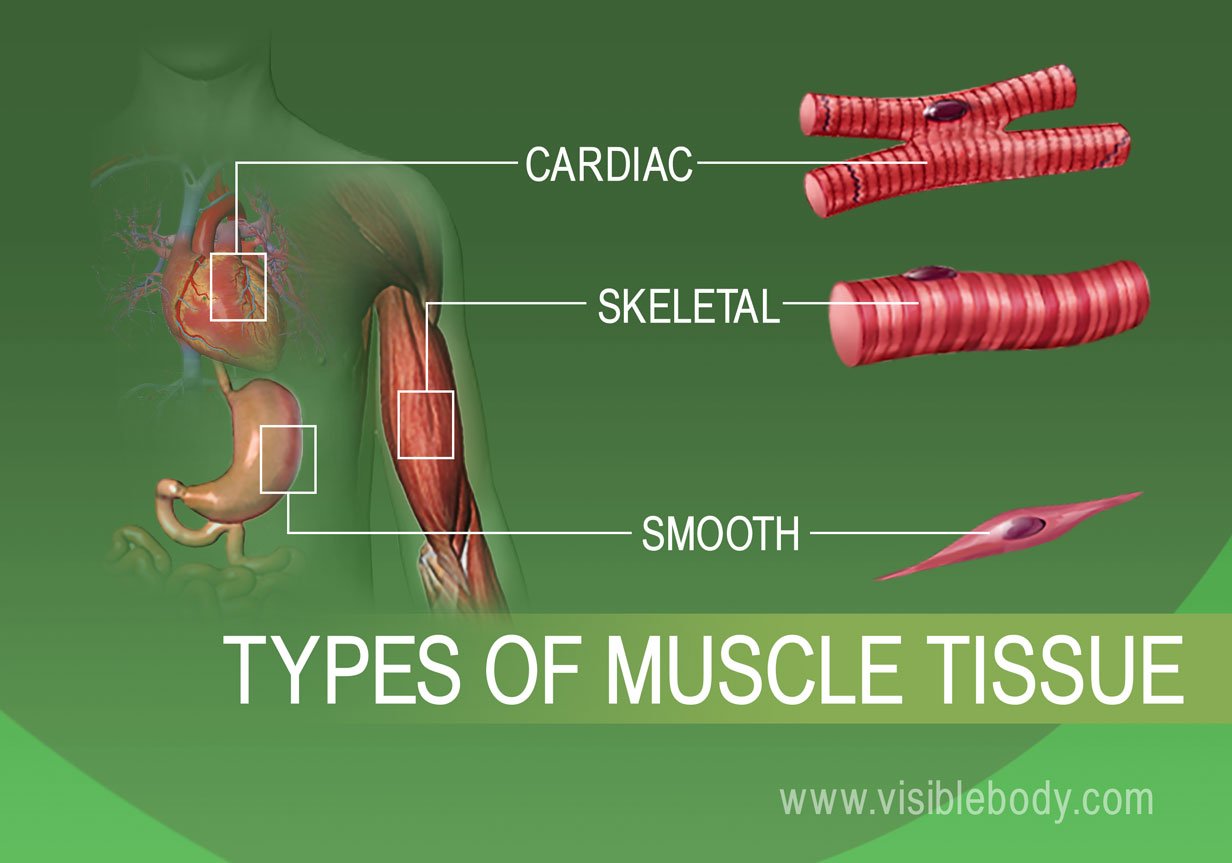
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/skeletal-muscle/0kdrKFzTosiUmeSgQIFJjQ_Skeletal_muscle_01.png)






Komentar
Posting Komentar